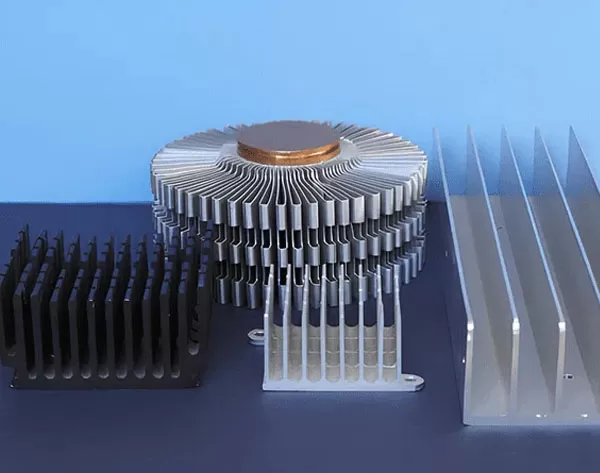
1. Pin-Fin Heatsinks
Design: Features an array of small, vertical pins extending from the base.
Advantages: Increases surface area for better heat dissipation. Ideal for applications requiring high airflow, such as servers or high-power LEDs.
Innovation: Optimized pin density and height for specific airflow conditions.
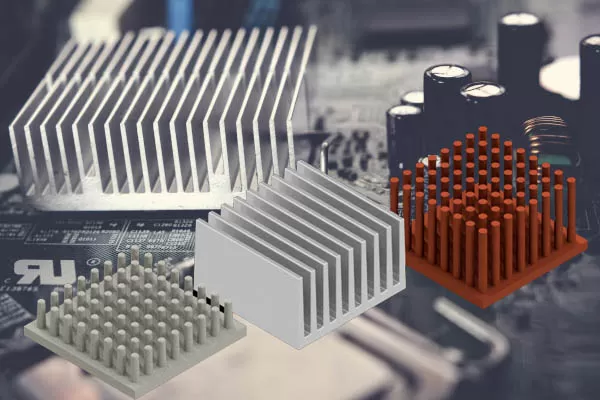
2. Wave-Fin Heatsinks
Design: Fins are shaped in a wave or zigzag pattern rather than straight.
Advantages: Enhances turbulence in airflow, improving heat transfer efficiency.
Innovation: Customizable wave patterns to match specific thermal and aerodynamic requirements.
3. Stacked Fin Heatsinks
Design: Multiple thin fins are stacked together to form a dense heatsink structure.
Advantages: Maximizes surface area while maintaining a compact form factor.
Innovation: Use of bonding techniques (e.g., epoxy or brazing) to securely attach fins without compromising thermal conductivity.
4. Skived Fin Heatsinks
Design: Fins are cut and lifted from a solid aluminum block using a skiving process.
Advantages: Extremely thin and tightly spaced fins for high heat dissipation in limited spaces.
Innovation: Precision skiving allows for unique fin shapes and configurations.
5. Hybrid Heatsinks
Design: Combines extruded aluminum with other materials (e.g., copper inserts or heat pipes).
Advantages: Leverages the strengths of multiple materials for superior thermal performance.
Innovation: Integration of heat pipes or vapor chambers into the extruded aluminum base for targeted heat spreading.
6. Asymmetric Fin Heatsinks
Design: Fins are unevenly spaced or shaped to optimize airflow and heat dissipation.
Advantages: Improves thermal performance in systems with non-uniform heat distribution or directional airflow.
Innovation: Custom fin arrangements tailored to specific device layouts.
7. Curved or Radial Heatsinks
Design: Fins are arranged in a circular or curved pattern around a central core.
Advantages: Ideal for applications with radial airflow, such as fans or blowers.
Innovation: Curved designs can be integrated into cylindrical devices like LED bulbs or motors.
8. Modular Heatsinks
Design: Consists of multiple extruded sections that can be assembled or stacked.
Advantages: Offers flexibility in size and shape, allowing for customization based on thermal requirements.
Innovation: Interlocking designs or snap-fit mechanisms for easy assembly and scalability.
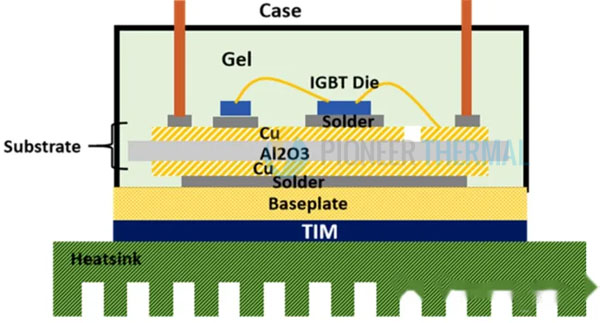
Additional Considerations
Surface Treatments: Anodizing or coating to improve corrosion resistance and thermal emissivity.
Custom Profiles: Tailored extrusion designs to fit specific applications or enclosures.
Lightweighting: Hollow or ribbed structures to reduce weight without compromising performance.
These innovative designs demonstrate how extruded aluminum heatsinks can be adapted to meet the evolving demands of modern thermal management systems.


 +86-18902844286
+86-18902844286
 E-mail
E-mail
