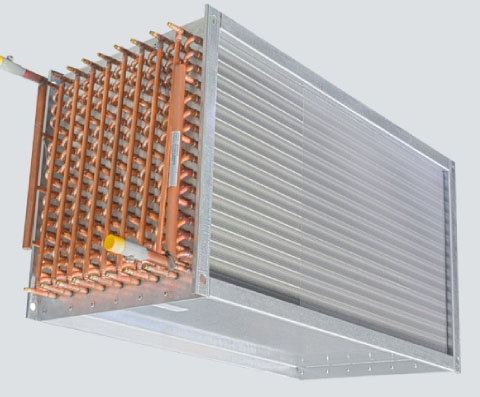
Finned tube heat sinks are divided into four ways: evaporative cooling, air cooling, water cooling and heat pipe cooling. The following is a detailed introduction of these four methods. Finned tube heat sink evaporative cooling, finned tube heat sink evaporative cooling, also known as natural cooling, generally through the natural convection of the air, the heating core part of the electronic component is contacted with the profile radiator. Its advantages are simple structure, convenient installation and low price. Finned tube heat sink is air-cooled for heat dissipation, and finned tube air-cooled for heat dissipation is a relatively common heat dissipation method at present.
Tube oxygen corrosion of finned tube heat sink has always been a key problem to be solved in the industry. It is very important to the existing technology development if we want to deal with the corrosion problem of finned tubes in the environment of oxygen-containing media. But as far as the current management level and capital conditions are concerned, the internal corrosion of finned tubes can be prevented first. At present, steel-aluminum finned tubes (wound steel-aluminum composite finned tubes, rolled steel-aluminum composite finned tubes) are widely used in finned tube radiators. It uses the compression resistance of steel pipe and the thermal conductivity of aluminum, and is compounded on a special machine tool. Its contact thermal resistance is almost zero at 210°C, not a general air heater.


 +86-18902844286
+86-18902844286
 E-mail
E-mail
