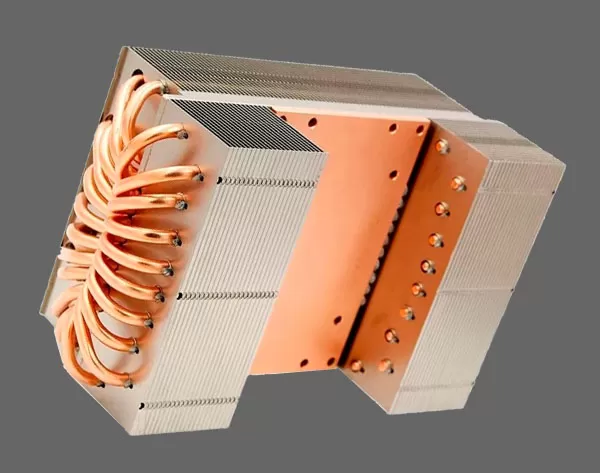
Integrated heat sink is a kind of part that plays an important role in the field of system integration. It is mainly used to dissipate the heat generated during the operation of the system to ensure the stable operation and performance of the system.
1. Working principle
Integrated heat sink usually transfers heat from the heat source to the surrounding environment by heat conduction, convection and radiation. For example, in the electronic equipment system, the heat sink is in close contact with the heating element and conducts the heat to the heat sink. Then, the heat is dissipated into the surrounding air or other cooling medium by air convection or liquid circulation.
2. Type
Air-cooled heat sink
Air-cooled heat sink is the most common type of integrated heat sink. It blows air through the radiator through the fan to accelerate the dissipation of heat. Air-cooled heat sink has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and easy installation, but the heat dissipation effect is relatively limited, and it is suitable for systems with less heat generation.
The materials of its heat sink are usually aluminum, copper, etc. Aluminum heat sink is light and cheap, but the heat dissipation performance is relatively weak; copper heat sink has better heat dissipation performance, but the price is higher.
Liquid-cooled heat sink
Liquid-cooled heat sink takes away heat through liquid circulation. It usually consists of a water pump, a radiator, pipes, etc. The heat dissipation effect of a liquid-cooled radiator is better than that of an air-cooled radiator, and it can meet the needs of systems with high heat generation. However, the cost of a liquid-cooled radiator is high, and the installation and maintenance are relatively complicated.
The choice of coolant is also very important. Common coolants include distilled water, ethylene glycol, etc. Distilled water has good heat dissipation performance, but it is easy to evaporate and leak; the heat dissipation performance of ethylene glycol is slightly inferior to distilled water, but it has good antifreeze and stability.
3. Application fields
Electronic equipment
In electronic equipment such as computers, servers, and communication equipment, system integrated radiators are used to dissipate the heat generated by components such as processors, graphics cards, and power supplies to prevent equipment from overheating and damage.
For example, high-performance computers usually use liquid-cooled radiators to ensure the stable operation of the processor, while ordinary home computers mostly use air-cooled radiators.
Industrial automation
In industrial automation control systems, various controllers, drivers, sensors and other devices also need radiators to dissipate heat. These devices usually work in harsh environments, generate a lot of heat, and have high performance requirements for heat sinks.
For example, in the factory's automated production line, devices such as PLC (programmable logic controller) require reliable radiators to ensure long-term stable operation.
New energy field
In solar energy, wind energy and other new energy power generation systems, inverters, controllers and other devices also need radiators to dissipate heat. These devices are usually installed outdoors, and the ambient temperature varies greatly, which requires high weather resistance and heat dissipation performance of the radiator.
For example, solar inverters usually use high-efficiency air-cooled radiators or liquid-cooled radiators to ensure normal operation in high temperature environments.
4. Selection points
○ Heat dissipation performance
According to the system's heat generation and heat dissipation requirements, select a radiator with appropriate heat dissipation performance. You can refer to parameters such as the radiator's thermal resistance, heat dissipation area, air volume or flow rate to evaluate its heat dissipation performance.
○ Size and installation method
Consider the system's space limitations and installation requirements, and select a radiator with appropriate size and easy installation. Some radiators may require special mounting brackets or fixing methods, which need to be considered in advance.
○ Reliability and durability
Choose a reliable and durable radiator to ensure the long-term stable operation of the system. You can check the radiator's brand, reputation, warranty period and other information to evaluate its reliability and durability.
○ Cost
According to the budget of the system, choose a heat sinkwith high cost performance. Don't just look at the price, but also consider factors such as heat dissipation performance and reliability.
In short, the integrated heat sink plays a vital role in system integration. Choosing a suitable heat sink can effectively dissipate the heat generated by the system and improve the stability and performance of the system. When choosing a heat sink, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as heat dissipation performance, size, installation method, reliability and cost according to the specific needs and characteristics of the system.
1. Working principle
Integrated heat sink usually transfers heat from the heat source to the surrounding environment by heat conduction, convection and radiation. For example, in the electronic equipment system, the heat sink is in close contact with the heating element and conducts the heat to the heat sink. Then, the heat is dissipated into the surrounding air or other cooling medium by air convection or liquid circulation.
2. Type
Air-cooled heat sink
Air-cooled heat sink is the most common type of integrated heat sink. It blows air through the radiator through the fan to accelerate the dissipation of heat. Air-cooled heat sink has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and easy installation, but the heat dissipation effect is relatively limited, and it is suitable for systems with less heat generation.
The materials of its heat sink are usually aluminum, copper, etc. Aluminum heat sink is light and cheap, but the heat dissipation performance is relatively weak; copper heat sink has better heat dissipation performance, but the price is higher.
Liquid-cooled heat sink
Liquid-cooled heat sink takes away heat through liquid circulation. It usually consists of a water pump, a radiator, pipes, etc. The heat dissipation effect of a liquid-cooled radiator is better than that of an air-cooled radiator, and it can meet the needs of systems with high heat generation. However, the cost of a liquid-cooled radiator is high, and the installation and maintenance are relatively complicated.
The choice of coolant is also very important. Common coolants include distilled water, ethylene glycol, etc. Distilled water has good heat dissipation performance, but it is easy to evaporate and leak; the heat dissipation performance of ethylene glycol is slightly inferior to distilled water, but it has good antifreeze and stability.
3. Application fields
Electronic equipment
In electronic equipment such as computers, servers, and communication equipment, system integrated radiators are used to dissipate the heat generated by components such as processors, graphics cards, and power supplies to prevent equipment from overheating and damage.
For example, high-performance computers usually use liquid-cooled radiators to ensure the stable operation of the processor, while ordinary home computers mostly use air-cooled radiators.
Industrial automation
In industrial automation control systems, various controllers, drivers, sensors and other devices also need radiators to dissipate heat. These devices usually work in harsh environments, generate a lot of heat, and have high performance requirements for heat sinks.
For example, in the factory's automated production line, devices such as PLC (programmable logic controller) require reliable radiators to ensure long-term stable operation.
New energy field
In solar energy, wind energy and other new energy power generation systems, inverters, controllers and other devices also need radiators to dissipate heat. These devices are usually installed outdoors, and the ambient temperature varies greatly, which requires high weather resistance and heat dissipation performance of the radiator.
For example, solar inverters usually use high-efficiency air-cooled radiators or liquid-cooled radiators to ensure normal operation in high temperature environments.
4. Selection points
○ Heat dissipation performance
According to the system's heat generation and heat dissipation requirements, select a radiator with appropriate heat dissipation performance. You can refer to parameters such as the radiator's thermal resistance, heat dissipation area, air volume or flow rate to evaluate its heat dissipation performance.
○ Size and installation method
Consider the system's space limitations and installation requirements, and select a radiator with appropriate size and easy installation. Some radiators may require special mounting brackets or fixing methods, which need to be considered in advance.
○ Reliability and durability
Choose a reliable and durable radiator to ensure the long-term stable operation of the system. You can check the radiator's brand, reputation, warranty period and other information to evaluate its reliability and durability.
○ Cost
According to the budget of the system, choose a heat sinkwith high cost performance. Don't just look at the price, but also consider factors such as heat dissipation performance and reliability.
In short, the integrated heat sink plays a vital role in system integration. Choosing a suitable heat sink can effectively dissipate the heat generated by the system and improve the stability and performance of the system. When choosing a heat sink, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as heat dissipation performance, size, installation method, reliability and cost according to the specific needs and characteristics of the system.


 +86-18902844286
+86-18902844286
 E-mail
E-mail
